
A high dividend yield could also suggest that a company is distributing too much profits as dividends rather than investing in growth opportunities or new projects. The dividend yield is a financial ratio that shows how much a company pays out in dividends each year relative to its stock price. The reciprocal of the dividend yield is the total dividends paid/net income which is the dividend payout ratio. It is pivotal to observe that one should keep a track-only of those shares which are constantly offering dividends to its shareholders.
Dividend Yields Make It Easy to Compare Stocks
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Companies in certain sectors of the economy tend to have higher dividends than others. That’s why it can help compare a company with its peers rather than the market.
The Wharton Online & Wall Street Prep Applied Value Investing Certificate Program
- Being one of the two main sources of returns for investing in the stock market, it would be unwise for you to neglect the returns from dividends.
- Dividend yield shows how much a company pays out in dividends relative to its stock price.
- For example, in the image below you can see the dividend yield listed for Duke Energy.
Dividend yield is the percentage of annual return in dividends on each dollar invested in the company. For example, if a company trades for $200 per share and that company pays a $2 annual dividend, then the company offers a 1% dividend yield. The dividend yield is calculated by dividing the annual dividend per share (DPS) by the current market share price and expressed as a percentage. A monthly dividend could result in a dividend yield calculation that is too low.
Related dividend stocks topics
But if the increase stems from a declining share price, that would be a concerning sign. For example, Companies A and B both pay an annual dividend of $2 dividend per share. Company A’s stock is priced at $50 per share, however, while Company B’s stock is priced at $100 per share. Company A’s dividend yield is 4% while Company B’s yield is only 2%, meaning Company A could be a better bet for an income investor. The dividend payout ratio is another way of looking at dividends, and in certain circumstances it may shed some light on whether a big dividend is sustainable.
US companies usually pay dividends on a quarterly basis, but sometimes they are paid on a monthly, semi-annual, or annual basis. Dividends can come in the form of cash payments or shares and are determined by the company’s board of directors. Dividends are a portion of a company’s earnings paid to investors and expressed as a dollar amount. Dividends are typically paid out each quarter (although semi-annual and monthly payouts are common). • Dividend yield represents the annual dividend paid to shareholders relative to the stock price, expressed as a percentage, which helps investors assess potential returns.
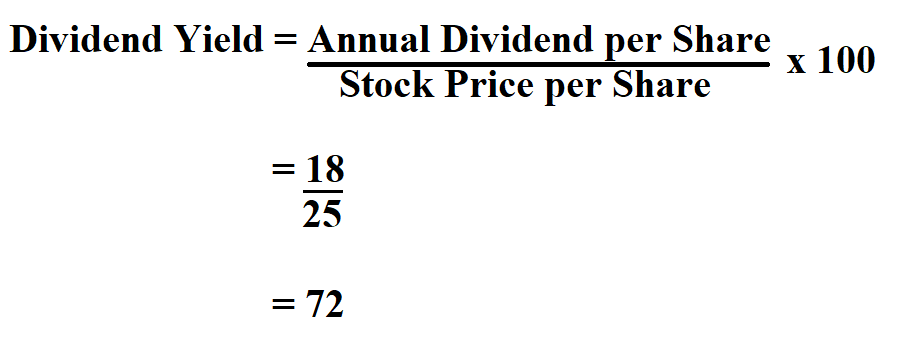
Dividend Payout Ratio (DPR)
The firm also decides to reinvest the other half to make some capital gains, increasing its value to $5.5 billion ($5billion + $500million) and appeasing its income investors. Dividend yields change and have an inverse relationship to the stock price. The yield rises when the price of the stock falls and falls when the price of the stock rises.
Investors who target having a minimum cash inflow from their investment portfolio can ensure this by making investments in stocks that regularly pay relatively high and stable dividend yields. It is a debatable statement that high dividends come at the cost of the firm’s growth potential. It is because every currency amount paid to the shareholders in the form of dividends is an amount that the company is not plowing back with an effort to increase its market share. High dividend yield stocks indicate how much a firm pays out in dividends about its market share price each year. It is a way to measure the cash flow ploughed back for every amount invested in the equity position.
That is why some people may refer to the dividend calculator as dividend reinvestment calculator. Some companies also offer DRIP opportunities (dividend reinvestment plans). a look at the renovation of the estate of things In such cases, instead of getting dividends from the company, it automatically gets reinvested into more shares, hence the other name of our tool – the DRIP calculator.
